In all programs conducted at our Vocational School, supporting theoretical education with practical training is adopted as a fundamental educational approach. In this context, practice-based, student-centered and skill-oriented teaching methods are effectively employed in courses to enhance students’ professional knowledge and skills.
Examples of teaching methods implemented within courses during the 2025–2026 academic year are summarized below.
In the Physiotherapy Program, within the course Basic Measurement and Evaluation in Physiotherapy, normal joint range of motion assessment methods were first addressed theoretically, followed by hands-on practical applications aimed at improving students’ assessment skills.
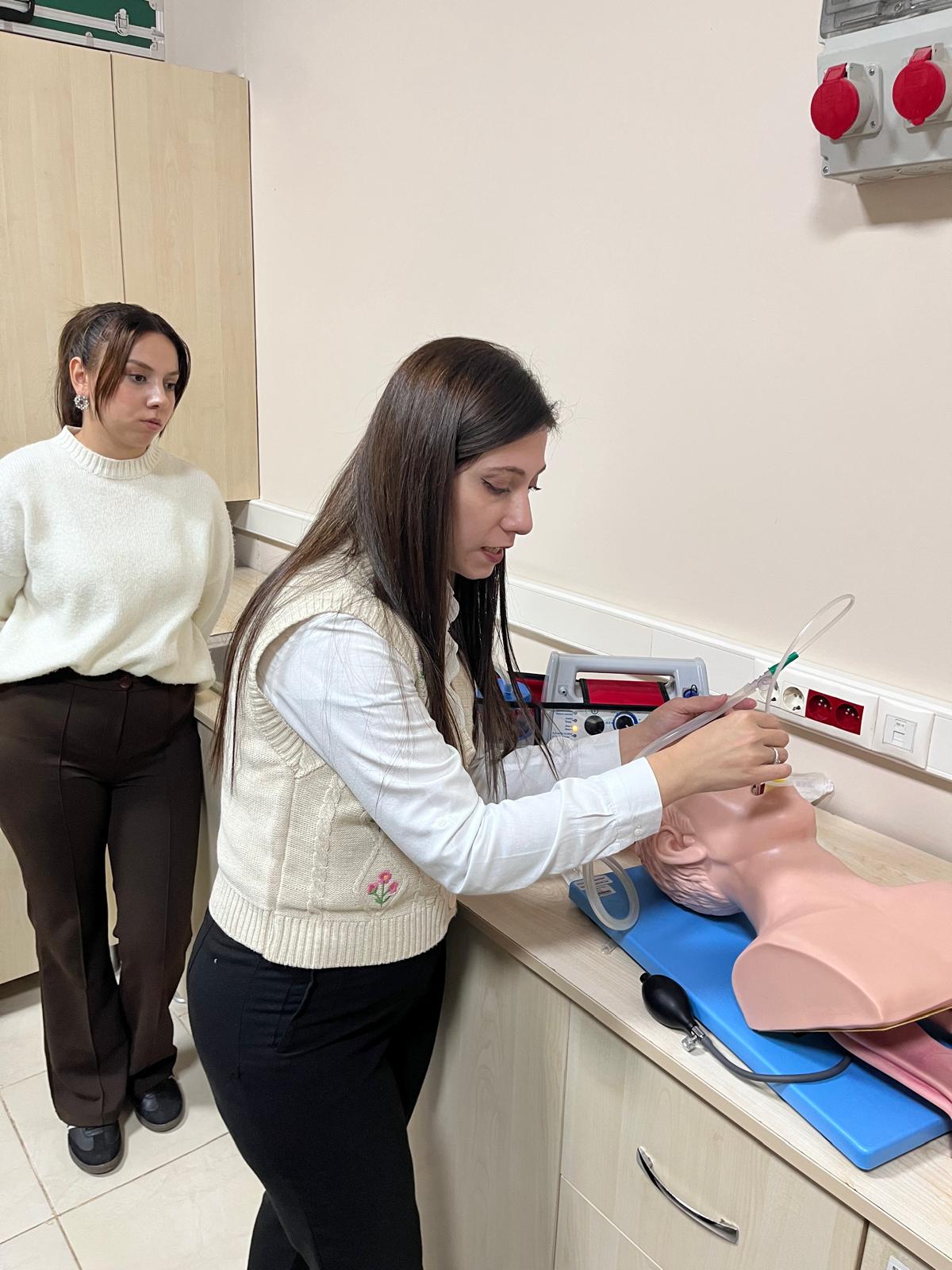
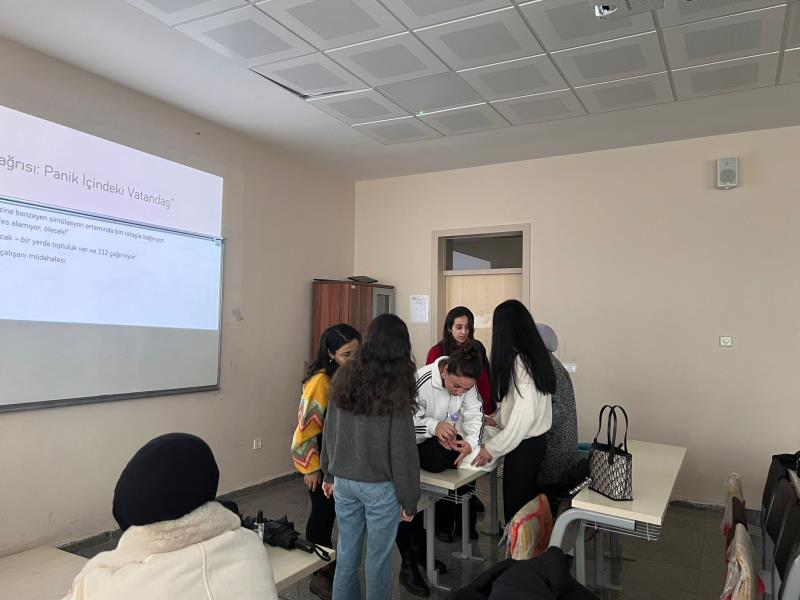
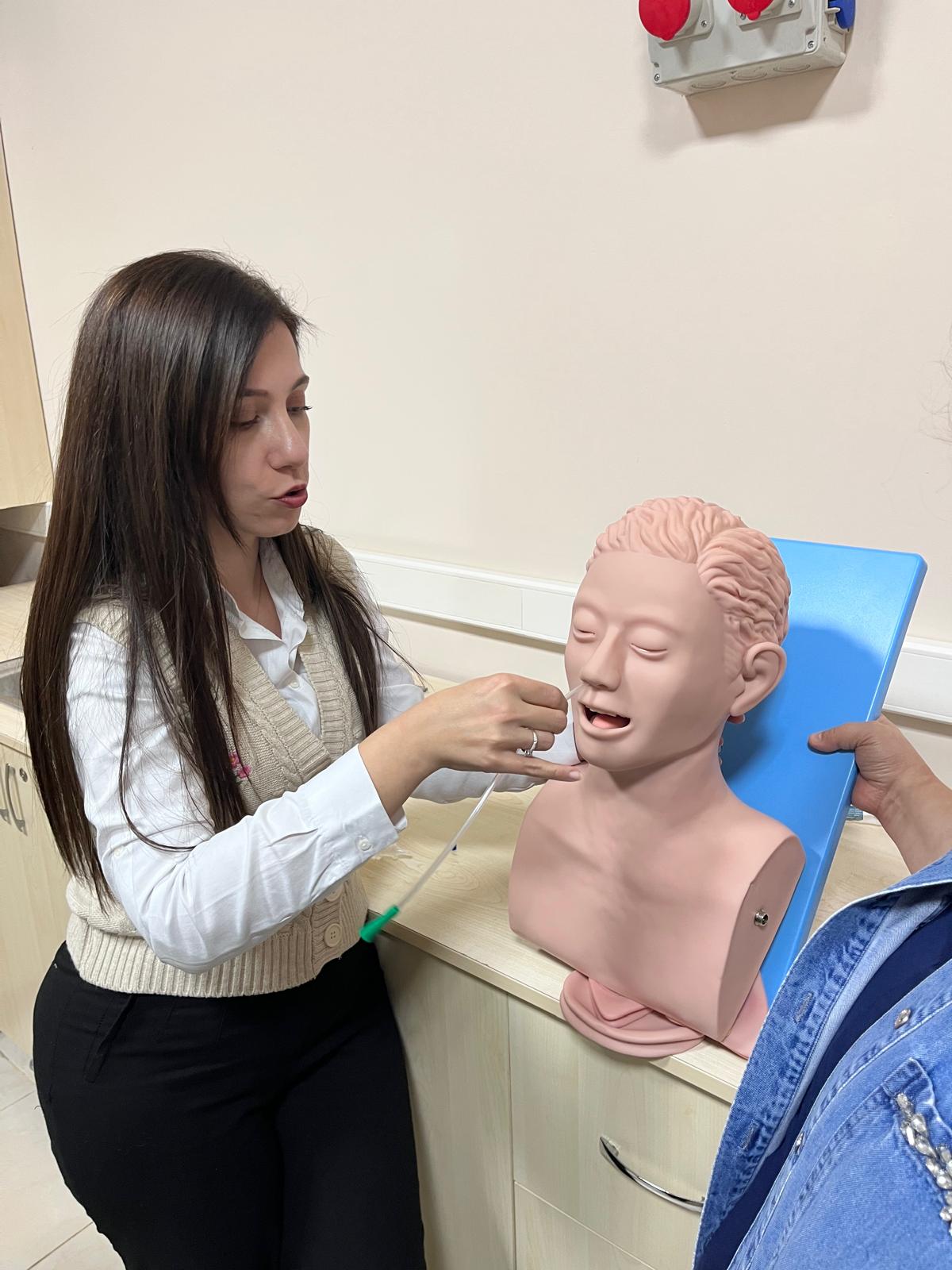
In the First and Emergency Aid Program, within the scope of the Resuscitation course, basic life support, cardiopulmonary resuscitation, and airway obstruction interventions for infants, children, and adults were carried out practically using simulation manikins.
In the Emergency Patient Care III course, the topic of childbirth and obstetric emergencies was first explained theoretically, followed by practical training on normal delivery processes and newborn care using training models.
Within the Advanced Life Support Practices course of the same program, critical interventions in emergency patient care were addressed through scenario-based and simulation-supported practices in addition to theoretical instruction. Students gained experience in CPR, intubation, and catheterization procedures using manikins.
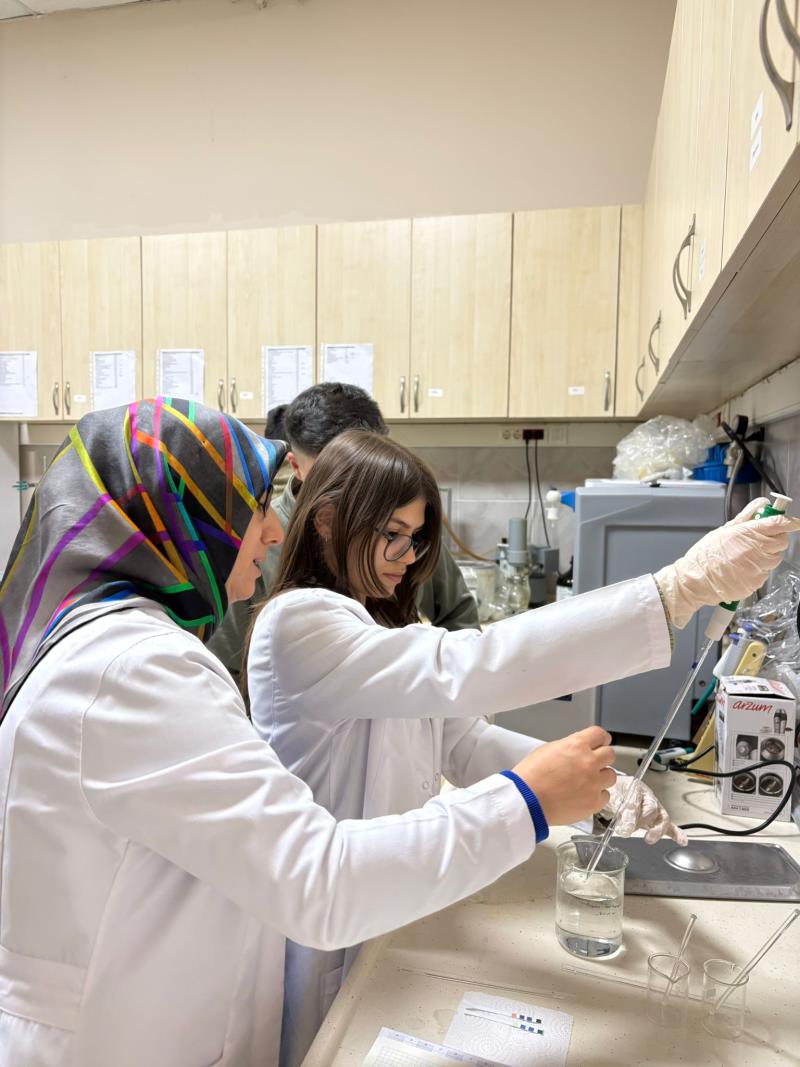
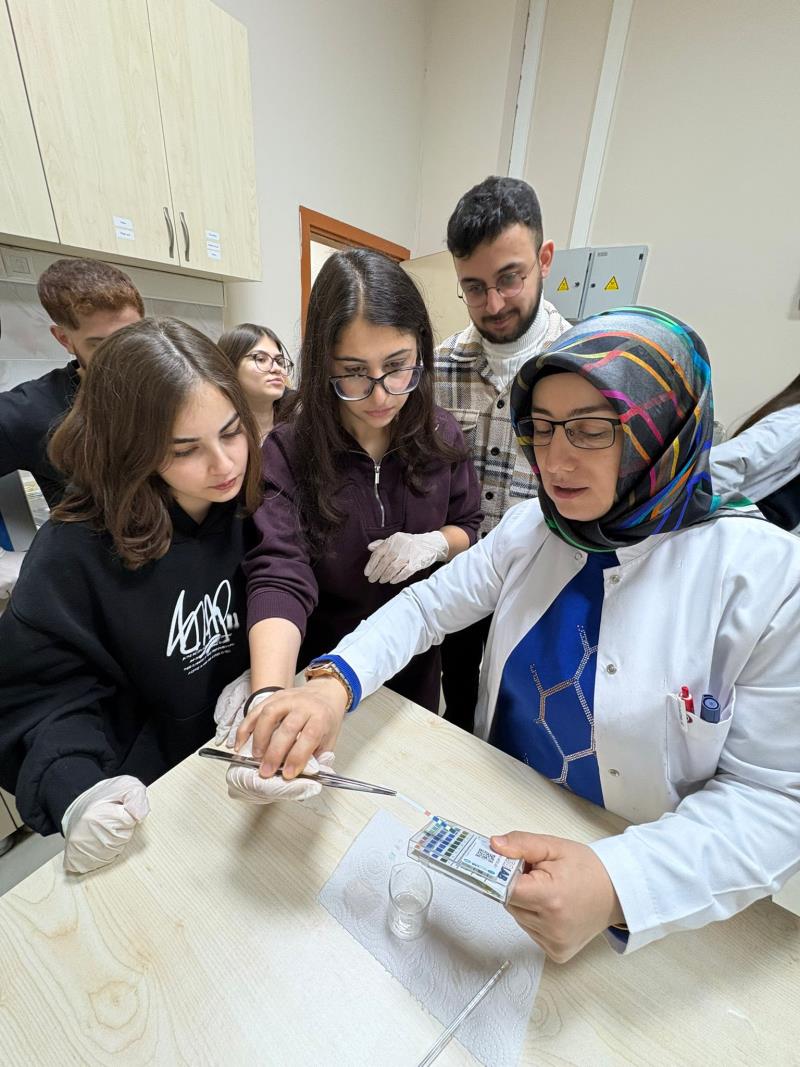
In the Medical Laboratory Techniques Program, within the Medical Laboratory course, practical experiments were conducted in our vocational school laboratories following theoretical instruction to reinforce students’ acquired knowledge.
Within this scope, students were asked to prepare solutions with specified pH values, the pH levels of the prepared solutions were determined using different measurement methods, and the experimental results were reported.
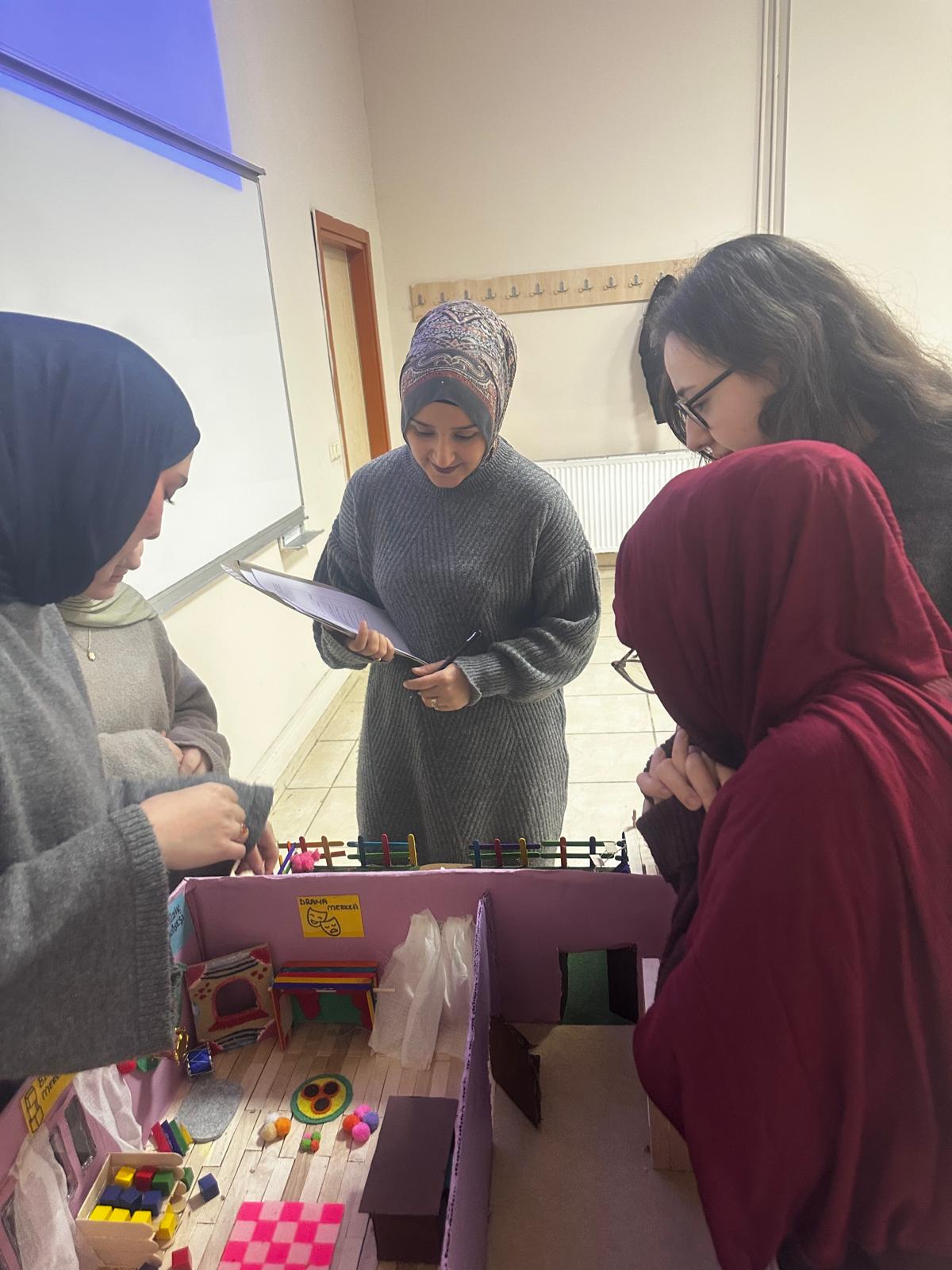
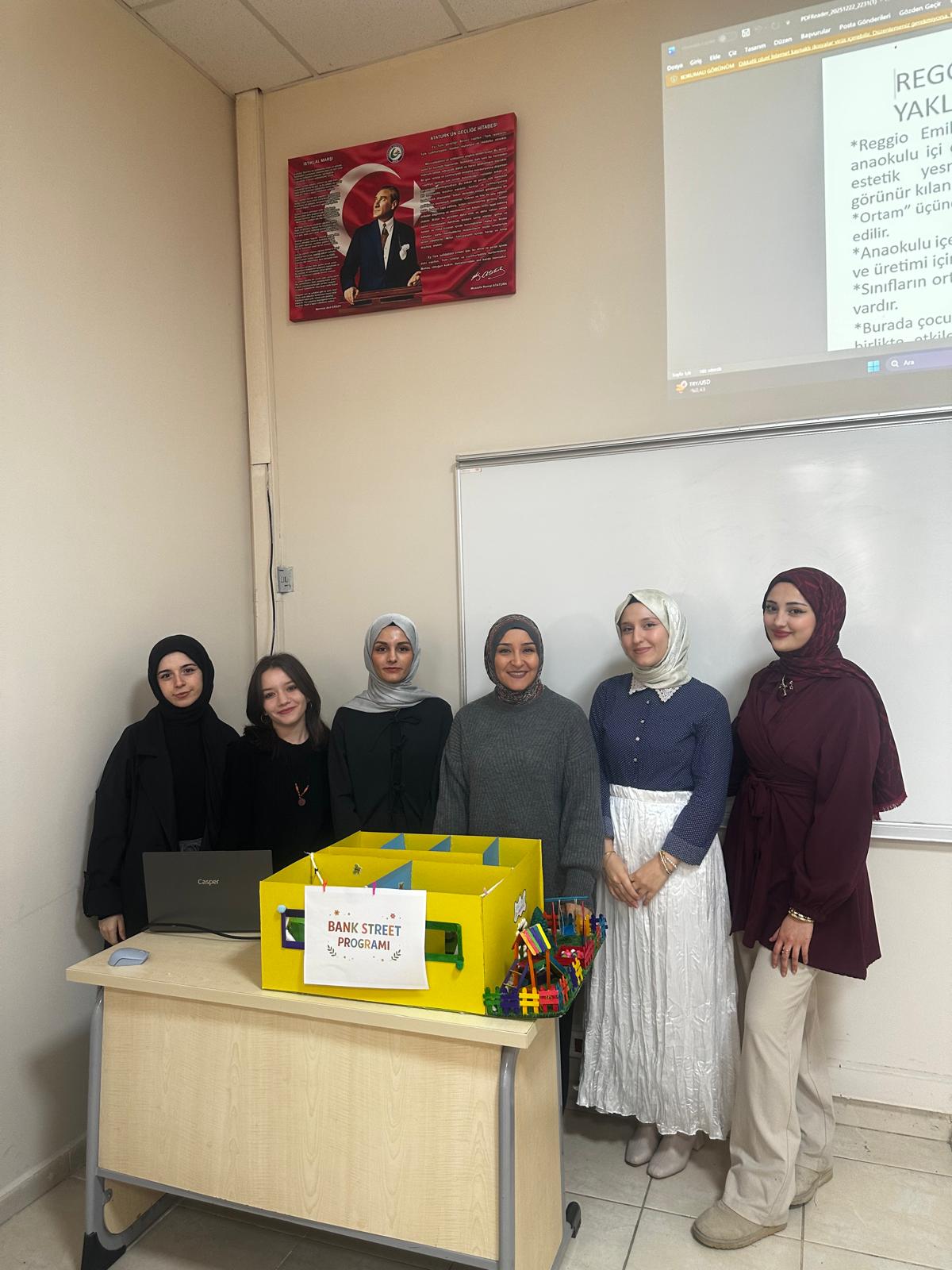
In the Child Development Program, within the course Different Approaches in Preschool Education, project and model studies related to kindergarten planning were carried out in accordance with the Montessori, High Scope, Bank Street, Waldorf, and Reggio Emilia approaches. Students presented their projects through oral presentations.
Within the Dialysis Program and the First and Emergency Aid Program, the course Psychology of Illness and Interpersonal Communication included mindfulness practices, emotion regulation activities, and structured group work aimed at improving students’ professional communication and psychosocial skills.
Through scenario-based practices involving interactions between patients, healthcare professionals, and patients’ relatives, the development of empathetic communication and crisis management skills was targeted. These applications aimed to transform theoretical knowledge into practice and strengthen students’ professional competencies.